Table of Contents
RFC 9470: OAuth 2.0 Step Up Authentication Challenge Protocol “introduces a mechanism for a resource server to signal to a client that the authentication event associated with the access token of the current request doesn’t meet its authentication requirements and specify how to meet them.” (excerpt from “Abstract”)
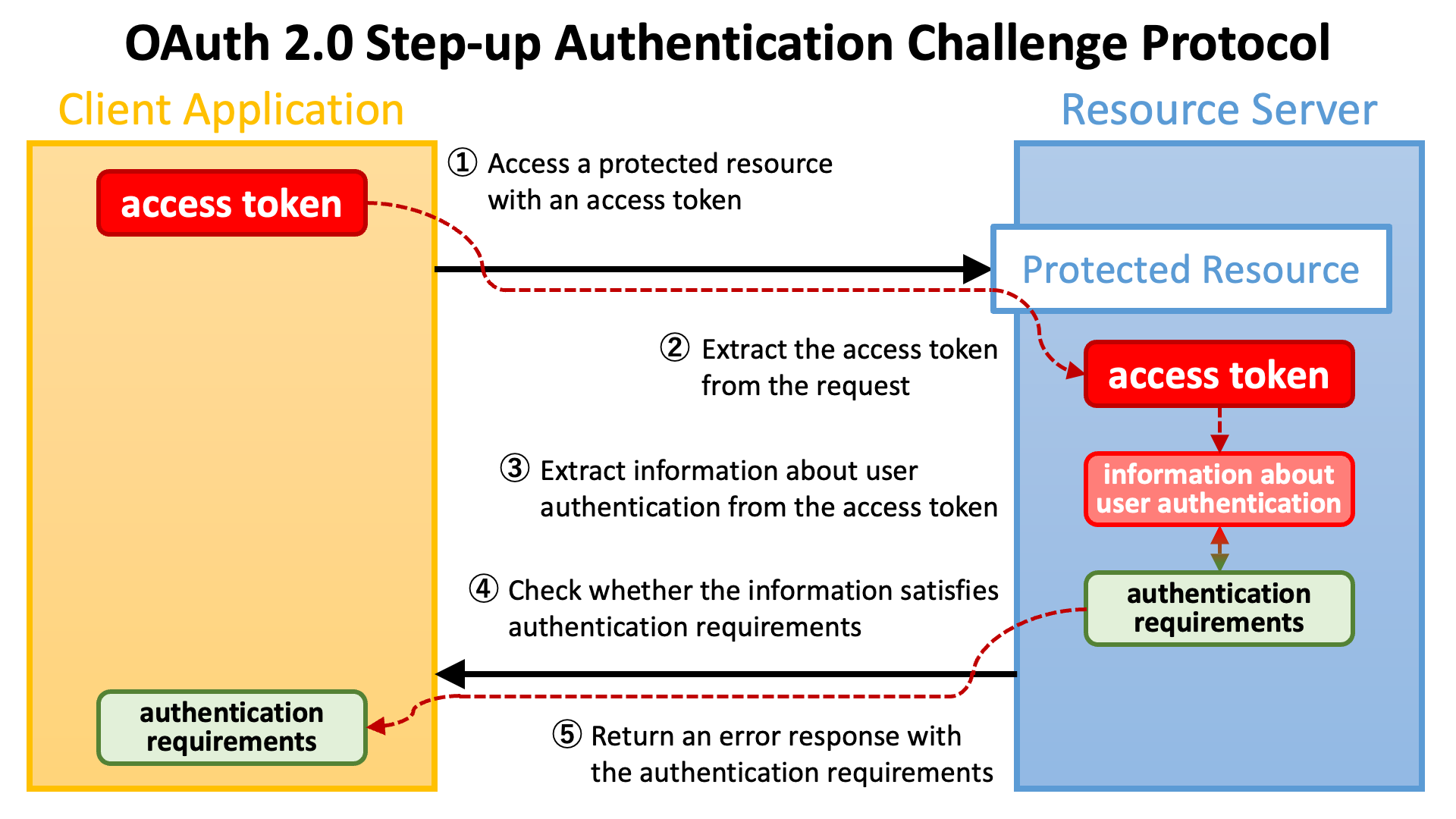
As the first step, a client application (a.k.a. relying party) accesses a protected resource endpoint with an access token.

The implementation of the endpoint extracts the access token from the request.

Next, the implementation of the endpoint extracts information about user authentication (which the authorization server performed during the course of issuing the access token) from the access token.

Then, the implementation of the endpoint checks whether the information about user authentication satisfies authentication requirements that the endpoint imposes.

If the requirements are not satisfied, the implementation of the endpoint returns an error response to the client application with information about the authentication requirements.

The diagram below illustrates the flow from making a request with an access token to returning an error response with authentication requirements.
After receiving an error response with authentication requirements, the client application will make an authorization request again. This time, the client application needs to ask the authorization server to issue an access token that satisfies the authentication requirements.

The OAuth 2.0 Step Up Authentication Challenge Protocol specification presumes two types of authentication requirements.
One is authentication context class reference (a.k.a. ACR) of user authentication. The other is maximum authentication age (a.k.a. max age) of user authentication.
User authentication is performed somewhere during an authorization flow. OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect do not define details about how to authenticate users, but client applications can specify criteria of user authentication by including a list of ACRs in an authorization request.
The authorization server tries to perform user authentication that satisfies at least one of the specified ACRs. However, no error is reported even if the authorization server cannot perform such user authentication unless the acr claim is requested as “essential” (described later).
acr_values Request ParameterThere are three ways to specify a list of ACRs. The first way is to use the acr_values request parameter. The parameter is defined in Section 3.1.2.1 of OpenID Connect Core 1.0 as follows.
acr_values: OPTIONAL. Requested Authentication Context Class Reference values. Space-separated string that specifies the acr values that the Authorization Server is being requested to use for processing this Authentication Request, with the values appearing in order of preference. The Authentication Context Class satisfied by the authentication performed is returned as the acr Claim Value, as specified in Section 2. The acr Claim is requested as a Voluntary Claim by this parameter.The value of the acr_values request parameter is a space-separated list of ACRs. It appears in an authorization request like the following.
https://as.example.com/authorize?acr_values=acr1+acr2+acr3&...
claims Request ParameterThe second way to specify a list of ACRs is to use the claims request parameter. The parameter is defined in Section 5.5 of OpenID Connect Core 1.0. The parameter takes a JSON object as a value and the syntax of the JSON is complex.
The following JSON is an example value of the claims request parameter excerpted from OpenID Connect Core 1.0.
{
"userinfo":
{
"given_name": {"essential": true},
"nickname": null,
"email": {"essential": true},
"email_verified": {"essential": true},
"picture": null,
"http://example.info/claims/groups": null
},
"id_token":
{
"auth_time": {"essential": true},
"acr": {"values": ["urn:mace:incommon:iap:silver"] }
}
}
This example specifies a list of ACRs that has just one element, urn:mace:incommon:iap:silver. When an authorization request includes this JSON as the value of the claims request parameter, the authorization server tries to perform user authentication that satisfies criteria of urn:mace:incommon:iap:silver.
To make the authorization server return an error when none of the specified ACRs can be satisfied, the client application must request the acr as an essential claim. By adding "essential":true in the JSON object that follows a claim name, the client application can request the claim as essential. In the example below, the auth_time claim and the acr claim are requested as essential.
{
"id_token":
{
"auth_time": {
"essential": true
},
"acr": {
"values": ["urn:mace:incommon:iap:silver"],
"essential": true
}
}
}
default_acr_values Client MetadataThe last way is to use the default_acr_values client metadata. The metadata is defined in Section 2 of OpenID Connect Dynamic Client Registration 1.0 as follows.
default_acr_values: OPTIONAL. Default requested Authentication Context Class Reference values. Array of strings that specifies the default acr values that the OP is being requested to use for processing requests from this Client, with the values appearing in order of preference. The Authentication Context Class satisfied by the authentication performed is returned as the acr Claim Value in the issued ID Token. The acr Claim is requested as a Voluntary Claim by this parameter. The acr_values_supported discovery element contains a list of the supported acr values supported by this server. Values specified in the acr_values request parameter or an individual acr Claim request override these default values.When an authorization request does not specify a list of ACRs explicitly, the value of the default_acr_values is, if set, used as a list of ACRs.
If the acr claim is requested as an essential claim, the authorization server returns an error response when none of specified ACRs can be satisfied. If the authorization server supports “OpenID Connect Core Error Code unmet_authentication_requirements”, unmet_authentication_requirements is used as the value of the error response parameter.

The following is the description about the error code in the specification.
unmet_authentication_requirements: The Authorization Server is unable to meet the requirements of the Relying Party for the authentication of the End-User. This error code SHALL be used if the Relying Party wants the OP to conform to a certain Authentication Context Class Reference value using an essential claim acr claim as specified in Section 5.5.1.1. of OpenID Connect Core [OpenID.Core] and the OP is unable to meet this requirement and MAY be used in other cases, if appropriate.If the authorization server does not support the specification, it is up to the authorization server what error code is used.
In the context of OpenID Connect Core 1.0, no error is reported even if the authorization server cannot perform such user authentication unless the acr claim is requested as essential.
However, OAuth 2.0 Step Up Authentication Challenge Protocol recommends that an ACR request by the acr_values request parameter (which requests the acr claim as a voluntary claim) be “treated as required” and the authorization server return the unmet_authentication_requirements error in case none of specified ACRs can be satisfied.
The recommendation slightly conflicts with the following paragraph excerpted from OpenID Connect Core 1.0.
Note that even if the Claims are not available because the End-User did not authorize their release or they are not present, the Authorization Server MUST NOT generate an error when Claims are not returned, whether they are Essential or Voluntary, unless otherwise specified in the description of the specific claim.
However, in practice, the slight conflict won’t be a big issue.
OpenID Connect Core 1.0 does not define actual ACR values. Therefore, to utilize ACR, it is necessary to define actual ACR values in a deployment-specific way. The following table shows examples of actual ACR values.
| Deployment | ACR Values |
|---|---|
| UK Open Banking | urn:openbanking:psd2:ca urn:openbanking:psd2:sca |
| AU CDR | urn:cds:au:cdr:2 urn:cds:au:cdr:3 |
| Open Banking Brasil | urn:brasil:openbanking:loa2 urn:brasil:openbanking:loa3 |
Authorization servers should advertise information about ACR values they support through their discovery documents. OpenID Connect Discovery 1.0 defines the acr_values_supported server metadata for the purpose as follows.
acr_values_supported: OPTIONAL. JSON array containing a list of the Authentication Context Class References that this OP supports.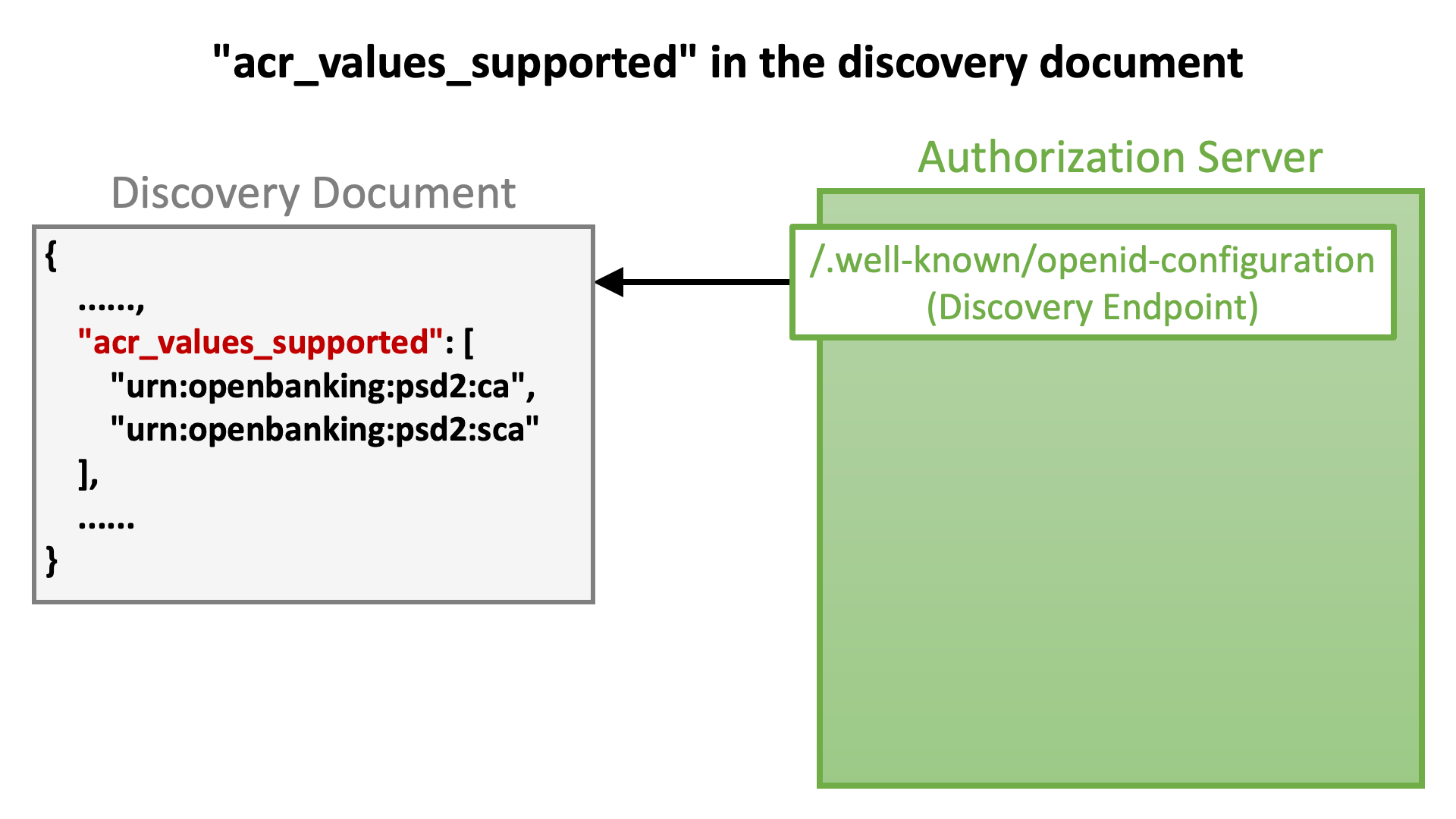
The previous section states “User authentication is performed somewhere during an authorization flow.” at the beginning. However, in practice, the authorization server may skip the user authentication process if it detects that a user has already been authenticated (= if a user has already logged in). Therefore, the time at which an authorization request was made is not necessarily equal to the time of user authentication that was performed for the authorization request.
The amount of time that has elapsed since the last user authentication is called “authentication age”. A client application may want to ask the authorization server to redo user authentication during an authorization flow in a case where the authentication age exceeds a particular threshold. The threshold is called “maximum authentication age”.
max_age Request ParameterSection 3.1.2.1 of OpenID Connect Core 1.0 defines the request parameter max_age as follows in order to enable client applications to specify the maximum authentication age.
max_age: OPTIONAL. Maximum Authentication Age. Specifies the allowable elapsed time in seconds since the last time the End-User was actively authenticated by the OP. If the elapsed time is greater than this value, the OP MUST attempt to actively re-authenticate the End-User. (The max_age request parameter corresponds to the OpenID 2.0 PAPE [OpenID.PAPE] max_auth_age request parameter.) When max_age is used, the ID Token returned MUST include an auth_time Claim Value.The value of the max_age is an integer that represents the maximum authentication age in seconds. It appears in an authorization request like the following.
https://as.example.com/authorize?max_age=600&...
default_max_age Client MetadataIf an authorization request does not contain the max_age request parameter but the default_max_age client metadata of the client is set, the value of the metadata is used as the maximum authentication age. The metadata is defined in Section 2 of OpenID Connect Dynamic Client Registration 1.0 as follows.
default_max_age: OPTIONAL. Default Maximum Authentication Age. Specifies that the End-User MUST be actively authenticated if the End-User was authenticated longer ago than the specified number of seconds. The max_age request parameter overrides this default value. If omitted, no default Maximum Authentication Age is specified.prompt Request ParameterWhen a client application wants to ask the authorization server to perform user authentication unconditionally (regardless of whether the maximum authentication age has been reached or not) during an authorization flow, it can use the prompt request parameter with the login value included. Its use will look like the following.
https://as.example.com/authorize?prompt=login&...
See Section 3.1.2.1 of OpenID Connect Core 1.0 for details about the prompt parameter.
Protected resource endpoints that utilize the OAuth 2.0 Step Up Authentication Challenge Protocol specification return an error response when the presented access token does not satisfy either or both of the authentication requirements (namely ACR and Max Age).
The diagram below illustrates the flow from returning an error response to making an authorization request asking for an access token that satisfies authentication requirements.

Parameters in the error response are explained in the subsequent sections.
insufficient_user_authentication Error CodeTo indicate that the reason of an error response is that authentication requirements are not satisfied, the specification defines an error code insufficient_user_authentication as follows.
insufficient_user_authentication: The authentication event associated with the access token presented with the request doesn’t meet the authentication requirements of the protected resource.The error code appears in the WWW-Authenticate HTTP header of an error response as shown below.
WWW-Authenticate: Bearer error="insufficient_user_authentication",...
acr_values ParameterTo list ACRs one of which an access token must satisfy, the specification defines a parameter acr_values as follows.
acr_values: A space-separated string listing the authentication context class reference values, in order of preference, one of which the protected resource requires for the authentication event associated with the access token.The parameter is used in conjunction with the error code insufficient_user_authentication like below (excerpt from the specification):
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized WWW-Authenticate: Bearer error="insufficient_user_authentication", error_description="A different authentication level is required", acr_values="myACR"
If a client application receives the error response above, the client application needs to make an authorization request that requests the acr claim as an essential with myACR included in values like below. Line-breaks in the example below are for display purposes only. An actual request does not contain line-breaks.
https://as.example.com/authorize?claims={
"id_token": {
"acr": {
"essential": true,
"values": [ "myACR" ]
}
}
}&...
max_age ParameterTo indicate the maximum authentication age which an access token must satisfy, the specification defines a parameter max_age as follows.
max_age: Indicates the allowable elapsed time in seconds since the last active authentication event associated with the access token.The parameter is used in conjunction with the error code insufficient_user_authentication like below (excerpt from the specification):
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized WWW-Authenticate: Bearer error="insufficient_user_authentication", error_description="More recent authentication is required", max_age="5"
If a client application receives the error response above, the client application needs to make an authorization request with the prompt request parameter with login included.
To enable protected resource endpoints to check whether a presented access token satisfies authentication requirements or not, the access token must hold information about the user authentication that was performed during the course of issuing the access token.
The OAuth 2.0 Step Up Authentication Challenge Protocol specification defines the following two attributes of access token that may appear in the payload part of JWT access tokens and the message body of token introspection responses (cf. RFC 7662).
| Attribute | Description (excerpted from the specification) |
|---|---|
acr |
Authentication Context Class Reference. String specifying an Authentication Context Class Reference value that identifies the Authentication Context Class that the user authentication performed satisfied. |
auth_time |
Time when the user authentication occurred. A JSON numeric value representing the number of seconds from 1970-01-01T00:00:00Z UTC until the time of date/time of the authentication event. |
The JSON below is an example excerpted from the specification that shows how the acr and auth_time attributes appear in the payload part of JWT access tokens.
{
"active": true,
"client_id": "s6BhdRkqt3",
"scope": "purchase",
"sub": "someone@example.net",
"aud": "https://rs.example.com",
"iss": "https://as.example.net",
"exp": 1639528912,
"iat": 1618354090,
"auth_time": 1646340198,
"acr": "myACR"
}
Authlete supports the OAuth 2.0 Step Up Authentication Challenge Protocol specification since version 2.3.
Some Authlete APIs such as the /auth/authorization/issue API accept the acr request parameter and the authTime request parameter which are used as values of the acr claim and the auth_time claim in the payload of an ID token being issued (cf. AuthorizationIssueRequest). Authlete 2.3 onwards binds information passed by the request parameters to an access token being issued, too.
The following set of shell commands simulates the authorization code flow (RFC 6749 Section 4.1) that issues an access token that holds information about ACR (acr) and authentication time (auth_time).
(1) Call the /auth/authorization API, which receives an authorization request as parameters and returns information about the request in JSON format (cf. AuthorizationResponse).
curl -v -X POST https://{api-cluster}.authlete.com/api/{serviceId}/auth/authorization \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-u 'Authorization: Bearer <Service Access Token e.g. Xg6jVpJCvsaXvy2ks8R5WzjdMYlvQqOym3slDX0wNhQ>' \ --data-urlencode parameters="response_type=code&scope=openid&client_id=${CLIENT_ID}&redirect_uri=${REDIRECT_URI}&state=${STATE}&claims={\"id_token\":{\"acr\":{\"essential\":true,\"values\":[\"${ACR}\"]}}}" > authorization_response.json
(2) Call the /auth/authorization/issue API, which receives a ticket issued by the /auth/authorization API as ticket, generates tokens (an authorization code, an access token, and/or an ID token), prepares an authorization response that conforms to related standard specifications, and returns JSON (cf. AuthorizationIssueResponse).
$ TICKET=`jq -r .ticket authorization_response.json`
$ AUTH_TIME=`date +%s`
$ curl -v -X POST https://{api-cluster}.authlete.com/api/{serviceId}/auth/authorization/issue \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-u 'Authorization: Bearer <Service Access Token e.g. Xg6jVpJCvsaXvy2ks8R5WzjdMYlvQqOym3slDX0wNhQ>' -d ticket=$TICKET -d subject=$SUBJECT -d authTime=$AUTH_TIME -d acr=$ACR > authorization_issue_response.json
(3) Call the /auth/token API, which receives a token request as parameters, generate tokens (an access token and optionally an ID token), prepares a token response that conforms to related standard specifications, and returns JSON (cf. TokenResponse).
$ AUTHORIZATION_CODE=`jq -r .authorizationCode authorization_issue_response.json`
$ curl -v -X POST https://{api-cluster}.authlete.com/api/{serviceId}/auth/token \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-u 'Authorization: Bearer <Service Access Token e.g. Xg6jVpJCvsaXvy2ks8R5WzjdMYlvQqOym3slDX0wNhQ>' \
--data-urlencode parameters="client_id=${CLIENT_ID}&grant_type=authorization_code&code=${AUTHORIZATION_CODE}&redirect_uri=${REDIRECT_URI}" -d clientId=${CLIENT_ID} -d clientSecret=${CLIENT_SECRET} > token_response.json
Instead of calling the /auth/authorization/issue API, the implementation of the authorization endpoint may call the /auth/authorization/fail API to indicate that the authorization request in question failed.
The /auth/authorization/fail API requires the reason request parameter that indicates the reason of the error (cf. AuthorizationFailRequest). When ACR_NOT_SATISFIED is specified as the value of the reason request parameter, Authlete 2.3 and newer versions prepare an error response whose error is unmet_authentication_requirements to conform to “OpenID Connect Core Error Code unmet_authentication_requirements”.
curl -v -X POST https://{api-cluster}.authlete.com/api/{serviceId}/auth/authorization/fail \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-u 'Authorization: Bearer <Service Access Token e.g. Xg6jVpJCvsaXvy2ks8R5WzjdMYlvQqOym3slDX0wNhQ>' \
-d ticket=$TICKET -d reason=ACR_NOT_SATISFIED > authorization_fail_response.json
The responseContent parameter in the response from the /auth/authorization/fail API is a URL that points to the redirection endpoint of the client application with the error and other parameters (cf. AuthorizationFailResponse).
$ jq -r .responseContent authorization_fail_response.json
http://localhost:4000/api/mock/redirection/4803170471?error=unmet_authentication_requirements&error_description=%5BA060305%5D+The+authorization+request+requests+%27acr%27+as+essential%2C+but+the+authentication+performed+for+the+end-user+satisfies+none+of+the+requested+ACRs.&error_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fdocs.authlete.com%2F%23A060305&state=917bdc1ef38ba6f6c297b4e31ac84007&iss=https%3A%2F%2Fauthlete.com
The URL contains the error_description parameter unless the errorDescriptionOmitted property of the Service is true (cf. Service.isErrorDescriptionOmitted()). The following is the URL-decoded value of the error_description parameter.
[A060305] The authorization request requests ‘acr’ as essential, but the authentication performed for the end-user satisfies none of the requested ACRs.
The format of access tokens issued by Authlete is configurable. When the accessTokenSignAlg property of Service is set (cf. Service.getAccessTokenSignAlg()), the format of access tokens is JWT (cf. “Enabling JWT-based access tokens”). Authlete 2.3 and newer versions embed the acr and auth_time claims into the payload of JWT access tokens as defined in the specification.
When the service is configured to generate JWT access tokens, the jwtAccessToken response parameter in responses from the /auth/token API holds a JWT access token (cf. TokenResponse).
$ JWT_AT=`jq -r .jwtAccessToken token_response.json`
If you decode the payload part of the JWT access token,
$ echo $JWT_AT | ruby -paF\\. -rbase64 -e '$_=Base64.urlsafe_decode64 $F[1]' | jq .
you will find that the acr claim and the auth_time claim are embedded there.
{
"sub": "taka",
"acr": "acr1",
"scope": "openid",
"auth_time": 1667321595,
"iss": "https://authlete.com",
"exp": 1667408271,
"iat": 1667321871,
"client_id": "5575687621",
"jti": "A1pURs-TMuyvueCoP2mSsntQX4-0IvYxlvectI4E2h8"
}
Authlete-powered authorization servers can implement a token introspection endpoint that conforms to RFC 7662 by using Authlete’s /auth/introspection/standard API. Implementations of protected resource endpoints may use the token introspection endpoint to get detailed information about access tokens.
The /auth/introspection/standard API receives a token introspection request as parameters and returns JSON (cf. StandardIntrospectionResponse).
$ AT=`jq -r .accessToken token_response.json`
$ curl -v -X POST https://{api-cluster}.authlete.com/api/{serviceId}/auth/introspection/standard \
-H "Content-Type:application/json" \
-u 'Authorization: Bearer <Service Access Token e.g. Xg6jVpJCvsaXvy2ks8R5WzjdMYlvQqOym3slDX0wNhQ>' \
--data-urlencode parameters="token=${AT}" > introspection_standard_response.json
The JSON contains the responseContent parameter. The value of the parameter is a JSON string that conforms to RFC 7662.
The following command line extracts the value of responseContent and parses it as JSON.
$ jq -r .responseContent introspection_standard_response.json | jq .
The result of the command line above will look like below. You can find the acr property and the auth_time property there.
{
"sub": "taka",
"acr": "acr1",
"scope": "openid",
"auth_time": 1667321595,
"iss": "https://authlete.com",
"active": true,
"token_type": "Bearer",
"exp": 1667408271,
"client_id": "5575687621"
}
Authlete provides the /auth/introspection API, which is also for access token introspection but different from the standard introspection endpoint.
Major advantages of the /auth/introspection API over the standard introspection endpoint are as follows.
The /auth/introspection API accepts the following request parameters as of this writing (cf. IntrospectionRequest).
| Parameter | Category | Version | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
token |
Common | 1.1 | An access token to introspect. |
scopes |
Common | 1.1 | Scopes that should be covered by the access token. |
subject |
Common | 1.1 | The subject (user identifier) that should be associated with the access token. |
clientCertificate |
RFC 8705 | 2.0 | The client certificate used in the mutual TLS connection established between the client application and the protected resource endpoint. |
dpop |
DPoP | 2.2 | The value of the DPoP HTTP header. |
htm |
DPoP | 2.2 | The HTTP method of the request to the protected resource endpoint. |
htu |
DPoP | 2.2 | The URL of the protected resource endpoint. |
resources |
RFC 8707 | 2.2 | Resource indicators that should be covered by the access token. |
targetUri |
2.3 | The full URL of the request. | |
headers |
HTTP Msg Sig | 2.3 | The HTTP headers to be included in processing the signature. |
requestBodyContained |
HTTP Msg Sig | 2.3 | Whether the request contains a message body. |
acrValues |
Step Up Auth | 2.3 | The list of Authentication Context Class Reference values one of which the user authentication performed during the course of issuing the access token must satisfy. |
maxAge |
Step Up Auth | 2.3 | The maximum authentication age which is the maximum allowable elapsed time since the user authentication was performed during the course of issuing the access token. |
Request parameters except token are related to access token validation. Ones to pay attention to here are the acrValues request parameter and the maxAge request parameter.
If the acrValues request parameter is supplied, the /auth/introspection API checks whether the ACR bound to the given access token is included in the acrValues array. If the ACR is not included, the API prepares an error response that conforms to the OAuth 2.0 Step Up Authentication Challenge Protocol specification.
The following command line lets the /auth/introspection API validate ACR.
$ curl -v -X POST https://{api-cluster}.authlete.com/api/{serviceId}/auth/introspection \
-H 'Content-Type:application/json' \
-u 'Authorization: Bearer <Service Access Token e.g. Xg6jVpJCvsaXvy2ks8R5WzjdMYlvQqOym3slDX0wNhQ>' \
-d token=$AT -d acrValues="acrX acrY" > introspection_response-acrValues.json
The responseContent parameter in the response from the API (cf. IntrospectionResponse) holds a string that should be used as the value of the WWW-Authenticate HTTP header. You will see that (a) the value of error is insufficient_user_authentication and (b) acr_values is included.
$ jq -r .responseContent introspection_response-acrValues.json
Bearer error="insufficient_user_authentication",error_description="[A341302] The authentication context class 'acr1' of the user authentication that the authorization server performed during the course of issuing the access token is insufficient. User authentication of an access token must satisfy one of [acrX acrY] to access the protected resource.",error_uri="https://docs.authlete.com/#A341302",acr_values="acrX acrY"
If the maxAge request parameter is supplied, the /auth/introspection API checks whether the specified time has elapsed since the user authentication time bound to the given access token. If the time has elapsed, the API prepares an error response that conforms to the OAuth 2.0 Step Up Authentication Challenge Protocol specification.
The following command line lets the /auth/introspection API validate authentication time.
$ curl -v -X POST https://{api-cluster}.authlete.com/api/{serviceId}/auth/introspection \
-H 'Content-Type:application/json' \
-u 'Authorization: Bearer <Service Access Token e.g. Xg6jVpJCvsaXvy2ks8R5WzjdMYlvQqOym3slDX0wNhQ>' \
-d token=$AT -d maxAge=600 > introspection_response-maxAge.json
In this case, the string for the WWW-Authenticate HTTP header contains max_age.
$ jq -r .responseContent introspection_response-maxAge.json
Bearer error="insufficient_user_authentication",error_description="[A340301] The time of the user authentication that the authorization server performed during the course of issuing the access token is too old, so re-authentication is needed. The maximum authentication age (max_age) required by the protected resource is 600.",error_uri="https://docs.authlete.com/#A340301",max_age="600"
We released Authlete 3.0 in November 2024 (announcement). Naturally, it supports the OAuth 2.0 Step Up Authentication Challenge Protocol. Please take full advantage of it!